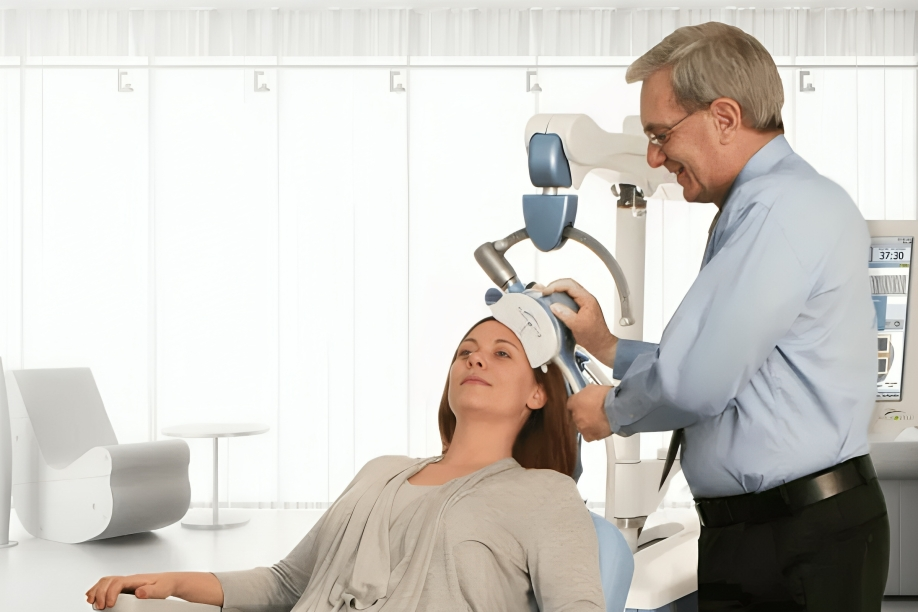
TMS, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a cutting-edge, non-invasive treatment that stimulates brain neurons with magnetic fields. TMS is often used to treat depression, especially when other therapies have failed. It works by targeting brain regions that regulate mood.
Throughout the therapy, a magnetic coil is placed on the scalp, producing pulses that trigger electrical activity in particular areas. The medicine is well accepted and has low side effects, making it an effective option for mental health therapy.
TMS Treatment APN
In TMS treatment, advanced practice nurses (APNs) play crucial roles by elevating professional understanding of mental health care. These specialists carry out thorough assessments to ascertain a patient’s eligibility for TMS and offer continuous assistance over the course of treatment. This innovative therapeutic technique provides a comprehensive strategy for treating mental health issues including anxiety and depression.
Benefits of TMS treatment
- Process that is non-invasive and doesn’t involve anesthetic.
- Very few adverse effects, most of which are transient and minor.
- For people with depression that is resistant to therapy, it is quite effective.
- Results that continue long after the course of treatment is over.
- Possibility of reducing obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and anxiety symptoms.
Role of APN

Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) are essential in the healthcare business because they provide exceptional care and support in a number of situations. Their primary duties include:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: APNs conduct comprehensive health evaluations, which include diagnostic testing and physical exams.
- Treatment Plans: They develop personalized treatment plans that may include therapeutic treatments and pharmacological prescriptions.
- Educating Patients: APNs provide important information regarding medical conditions, accessible therapies, and lifestyle modifications to help patients improve their health.
- Treatment coordination: They collaborate with other medical experts to ensure that patients receive comprehensive and continuous care.
APNs represent patients’ needs and preferences, ensuring that they have access to appropriate services and treatment.
How TMS treatment APN work
Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) do comprehensive evaluations to ascertain whether a patient is a suitable candidate for Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) treatment.
They tell patients about the TMS technique’s advantages, hazards, and potential adverse effects in order to get their informed consent. TMS-trained APNs oversee treatment sessions and attach the magnetic coil on the scalp correctly.
In addition to managing any adverse effects, they regularly evaluate the patient’s reactions and modify treatment plans as needed. Following TMS treatment APN stay involved by providing follow-up care to measure long-term results and continuing mental health assistance.
Process of TMS treatment APN
- Initial Consultation: The APN conducts a thorough review of the patient’s mental health history and present symptoms to evaluate whether TMS is a suitable therapy choice.
- Patient Education: The APN thoroughly describes the TMS process, including advantages, dangers, and predicted outcomes, so that the patient is completely educated and consents to the therapy.
- Treatment Planning: Working with the patient, the APN creates a tailored treatment plan that defines the frequency and length of TMS treatments depending on individual needs.
- Getting Ready for Sessions: On treatment days, the APN assures the patient’s comfort and optimum placement for successful TMS administration.
- TMS administration: The APN uses the TMS equipment to set the magnetic coil on the scalp and administer tailored magnetic pulses to activate particular brain locations.
- Monitoring Progress: Throughout the TMS session, the APN continuously monitors the patient’s comfort level and treatment reactions, making modifications as appropriate.
- Post-Treatment Assessment: Following each session, the APN assesses the patient’s responses and any side effects, discusses progress, and plans for future sessions.
- Ongoing Care: After TMS therapy, the APN continues to offer support by assessing long-term outcomes and changing mental health care plans as needed to ensure continuous recovery.
TMS Treatment APN vs. Traditional Treatment

- Non-Invasiveness: Unlike traditional treatments, which usually have systemic effects on the body, TMS is a non-invasive technique that stimulates brain activity using magnetic fields.
- focused Mechanism: While traditional medicines may address symptoms through chemical changes in the brain without focused stimulation, TMS selectively targets brain regions involved in mood control.
- Side Effects: When compared to other therapies, TMS has fewer and milder side effects, such as modest discomfort on the scalp.
- Treatment Duration: TMS treatments are generally 20 to 40 minutes long and spaced out over several weeks, whereas traditional therapy sometimes entail continuous medication delivery and regular visits to monitor success.
- Efficacy: TMS is extremely useful for those suffering from treatment-resistant depression, providing benefits where other medications may fail.
Read Also: Comprehensive Guide to the Benefits of Cloves
Future of TMS Treatment APN
TMS treatment APN is becoming increasingly vital, driving the therapy’s future potential. APNs’ clinical expertise and patient-first approach are expanding access to this innovative treatment for mental health conditions such as depression.
As TMS therapy evolves through new research and technological breakthroughs, APNs will play a pivotal role in its wider adoption and success, ensuring it becomes a mainstay in mental health care.